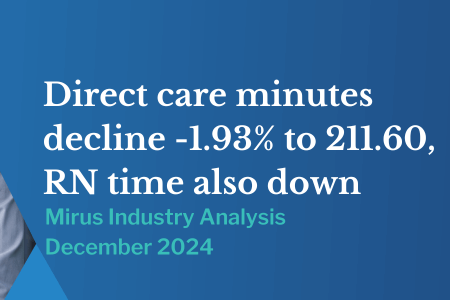
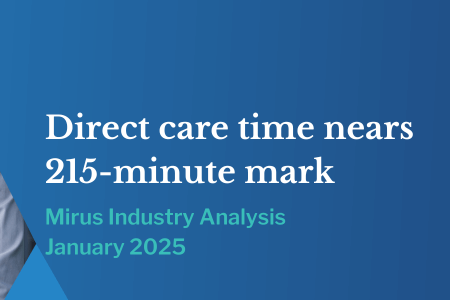What is Phishing? 6 top tips from our IT Manager, Security
April 6, 2020 | Technology

To further enhance our cyber defense, Sandeep V M, IT Manager, Security at Mirus Australia recently highlighted a common cyber-attack named – Phishing.
“Phishing” is the most common type of cyber-attack that can affect an organisation. Phishing attacks can take many forms, but they all share a common goal – to get you to share sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card information, or bank account details.
Although Mirus Australia maintain strict controls to help protect our networks and computers from cyber threats, we also rely on every team member to be our first line of defence.
Here Sandeep has outlined a few different types of phishing attacks to watch out for:
• Phishing: In this type of attack, hackers impersonate a real company to obtain your login credentials. You may receive an e-mail or SMS asking you to verify your account details with a link that takes you to an imposter login screen that delivers your information directly to the attackers.
• Spear Phishing: Spear phishing is a more sophisticated phishing attack that includes customised information that makes the attacker seem like a legitimate source. They may use your name and phone number and refer to your company name in the e-mail to trick you into thinking they have a connection to you, making you more likely to click a link or attachment that they provide.
• Whaling: Whaling is a popular ploy aimed at getting you to transfer money or send sensitive information to an attacker via email by impersonating a real company executive. Using a fake domain that appears similar to ours, they look like normal emails from a high-level official of the company, typically the CEO or CFO, and ask you for sensitive information (including usernames and passwords).
• Shared Document Phishing: You may receive an e-mail that appears to come from file-sharing site like SharePoint alerting you that a document has been shared with you. The link provided in these e-mails will take you to a fake login page that mimics the real login page and will steal your account credentials.
What You Can Do
To avoid these phishing schemes, please observe the following email best practices: Do not click on links or attachments from senders that you do not recognise. Be especially wary of .zip or other compressed or executable file types.
(1) Do not provide sensitive personal information (like usernames and passwords) over email.
(2) Watch for email senders that use suspicious or misleading domain names.
(3) Inspect URLs carefully to make sure they’re legitimate and not imposter sites.
(4) Do not try to open any shared document that you’re not expecting to receive.
(5) If you can’t tell if an email is legitimate or not, please forward them to your IT Managers
(6) Be especially cautious when opening attachments or clicking links if you receive an email containing a warning banner indicating that it originated from an external source.